In the pharmaceutical industry, data integrity and rights management are always critical, especially when it comes to devices and information systems. Many pharmaceutical enterprises have clearly put forward the requirement of "three-level authority" in device URS, but there is often a lack of uniform standards for the specific interpretation and implementation details of this requirement. As a result, there are great differences in the understanding and implementation of "three-level authority" among different companies. So what exactly is "three-level authority"? How to design and implement this permission framework to ensure system security and data integrity?
一、The source of "three-level authority"
1. Requirements for Drug Records and Data Management (Trial): "Article 22 Electronic records shall realize operation authority and user login management, at least including: establishing different authorities for operation and system management, and the user authority of the person in charge of the business process shall match the responsibilities undertaken." Do not give them the privileges of an administrator of the system (including the operating system, applications, databases, etc.); ".".
2. PIC/S Good Practice for Data Management and Integrity in a Regulated GMP/GDP Environment: "The system should support different user access roles (levels), and the assignment of roles should follow the least privilege rule, that is, the minimum access level necessary for any job function.". Simple systems should have at least regular and administrator users, but complex systems often require more levels of users (e.g., hierarchy) to effectively support access control.
3.PDA TR 84 "Application of Data Integrity Requirements in Manufacturing and Packaging": "Access control may be much less stringent for less critical systems, such as HMIs that control conveyor speeds but do not store data on auxiliary packaging lines. For these types of systems, passwords or group accounts may be used. However, there must be controls to ensure segregation of duties between user levels (i.e., Administrator vs. Engineer, Operator). Passwords or group accounts should be changed annually. These controls can also be used for other low-critical activities that do not require corresponding action. For example, when the system requires a login to activate the Stop 1 Start function, the group account can be used to press the Start/Stop button on the packaging line. From the relevant guidelines, it can be seen that for the system applied in pharmaceutical enterprises, it is necessary to separate the rights and responsibilities, that is, the corresponding responsibilities match the corresponding permissions. If ordinary users do not need to set equipment configuration parameters, they should not assign the permissions of configuration parameters to this user. User levels are described in the PIC/S guidelines as different hierarchies. If three levels are required, they may be colloquially referred to as "three-level permissions".
二、Whether the "three-level authority" set by the equipment is sufficient
In fact, it is not sufficient for the user to only require "three-level authority". The general "three-level authority" may not meet the minimum authority responsibility matching. Moreover, some devices can only carry out three-level authority, and can not set multi-level authority, which has certain risks. Therefore, it is not sufficient to describe only the "three-level authority" from the perspective of user requirements, at least the following requirements should be described:
1. Multi-layer classification requirements
It is described in multiple guidelines that there should be at least two obvious separation of duties, namely, management permissions and business permissions. If only management permissions and business permissions are required to be separated when requirements are proposed, business process owners need to have permissions other than management permissions, which will lead to the problem that account level settings do not conform to the separation of duties of the company's internal structure. Therefore, the two obvious separation of responsibilities is far from enough, and the requirements need to mention that the setting of the equipment account level should correspond to the division of responsibilities within the company. For example, a temperature and humidity online monitoring system can arbitrarily add, delete and edit permission level names in account level settings, and the number of level settings is not limited, which meets the corresponding responsibilities of the internal structure of the user company and achieves the separation of responsibilities. (See Figure below)
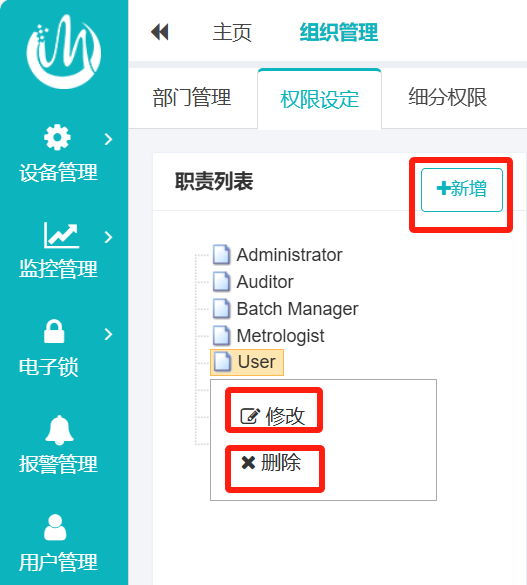
2. Focus on the separation of powers and responsibilities
Several levels of permissions are not the focus of attention, and the focus is to separate permissions. In addition to the above separation of management permissions and business permissions, business permissions should also be separated. The most basic function of general devices is to set menu access permissions. Can this function be met in practical application? This is generally considered for the positions that may be involved in the equipment.
Take a temperature and humidity online monitoring system as an example:
Ordinary user classification: menu access of equipment management/monitoring management/alarm management/data report;
QA/QC level: menu access for equipment management/monitoring management/alarm management/user management/annual calibration/audit trail/data report/organization management;
QA/QC manager level: menu access, addition, modification and electronic signature of equipment management/monitoring management/alarm management/user management/annual calibration/audit trail/data report/organization management;
Production/quality director level: menu access, addition, modification, deletion and electronic signature of equipment management/monitoring management/alarm management/user management/annual calibration/audit trail/data report/organization management;
IT administrator level: menu access, addition, modification, deletion, management and electronic signature of user management/basic setting/IOT platform/organization management.
It can be seen from the example that this system can customize the specific permission allocation of each level of users according to the requirements of the company's job responsibilities, so as to meet the separation of rights and responsibilities that the guide focuses on. This system function meets the user's needs in two forms:
(1) The software has a way to establish roles independently and assign permissions independently.
(2) Fixed roles match corresponding permissions.
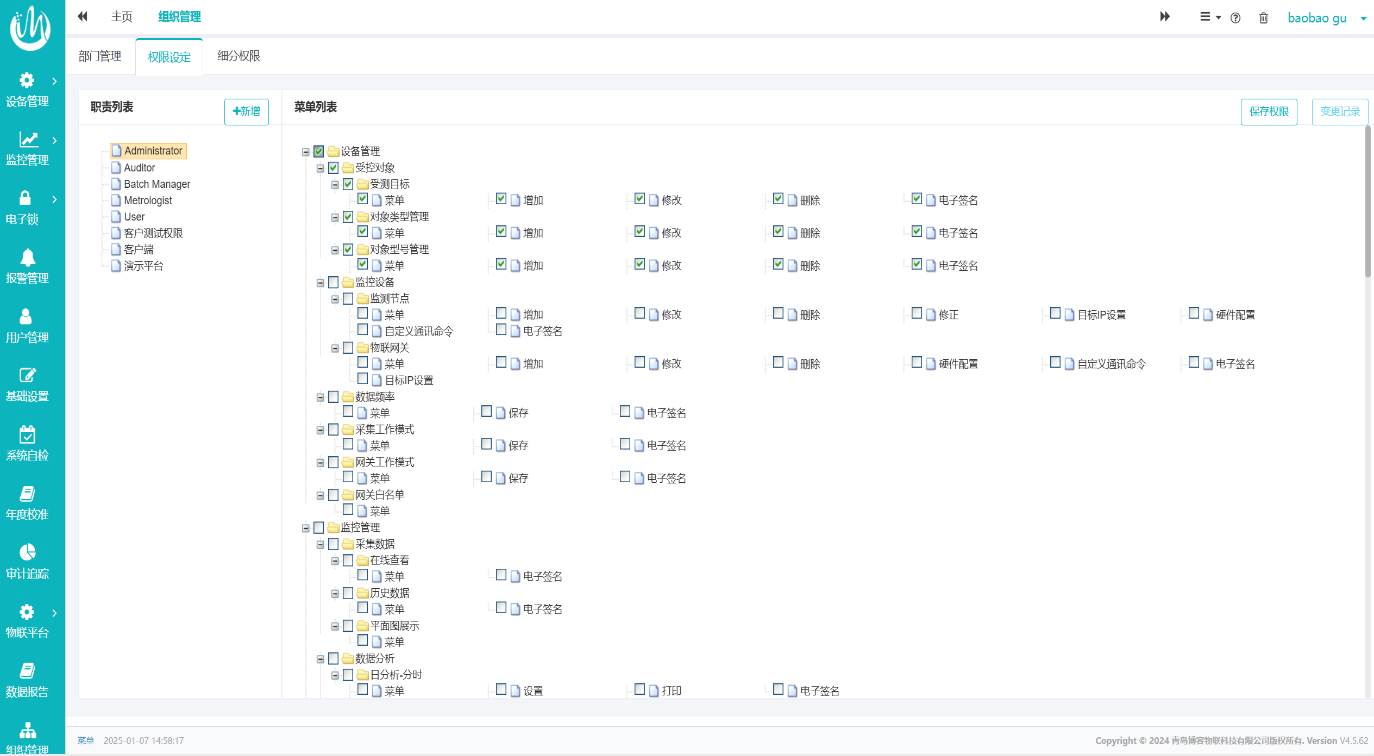
Generally speaking, "three-level authority" is a colloquial explanation. Equipment and information systems need to meet the minimum authority assignment and focus on the separation of powers and responsibilities to reduce risks. Therefore, it is very important to add, delete, edit user level names and customize the system design of user permissions at each level.
Copyright©2019Qingdao Biorong IoT Technology Co., Ltd All right reserved 鲁ICP备20030433号-1 Website Map